Types of Conveyor Belts
- Bhargava Krishna Marripati

- Sep 3, 2024
- 12 min read

Introduction to Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts play a crucial role in various industries, serving as the backbone of material handling and transportation systems. These versatile systems have revolutionized the way goods and materials are moved, significantly improving efficiency, productivity, and safety across diverse sectors.
In manufacturing plants, conveyor belts streamline the production process by seamlessly transporting raw materials, work-in-progress components, and finished products from one station to another. This continuous flow minimizes downtime and ensures a smooth and consistent workflow, contributing to increased output and cost-effectiveness.
Warehouses and distribution centers rely heavily on conveyor belts to expedite the sorting, routing, and loading of goods. These systems facilitate the rapid and organized movement of products, reducing manual labor and minimizing the risk of damage during handling.
The food processing industry benefits greatly from the use of conveyor belts, particularly those designed for sanitary environments. These specialized belts ensure the safe and hygienic transportation of food products, adhering to stringent regulations and maintaining the highest standards of cleanliness.
Beyond these industries, conveyor belts find applications in mining, agriculture, airports, and even recycling facilities, demonstrating their versatility and adaptability to diverse operational needs.
To meet the varying requirements of these industries, conveyor belts come in a wide range of types, each designed to cater to specific applications, load capacities, and environmental conditions. Understanding the different types of conveyor belts is essential for selecting the most suitable system for a particular operation, optimizing performance, and maximizing return on investment.
What is a Conveyor Belt?
A conveyor belt is a continuous, moving loop used to transport materials or products from one location to another. It consists of two or more pulleys (sometimes referred to as drums) that rotate and cause the belt to move. The belt itself is a flat, flexible surface made of various materials, such as rubber, plastic, or metal, depending on the application.
Conveyor belts have a long history dating back to the late 18th century when rudimentary systems were used in agriculture and mining operations. However, it wasn't until the late 19th century that conveyor belts became more widely adopted in industrial settings. The introduction of rubber and the development of efficient motor systems played a crucial role in the evolution of modern conveyor belt systems.
Over time, conveyor belts have undergone significant advancements in terms of materials, designs, and applications. Today, they are an essential component in numerous industries, ranging from manufacturing and logistics to food processing and airport baggage handling systems. The versatility and efficiency of conveyor belts have made them indispensable in streamlining operations and improving productivity across various sectors.
Roller Bed Conveyor Belts

Description and Applications:Roller bed conveyor belts, also known as roller conveyors, are a type of conveyor system that uses a series of parallel rollers to transport materials. These conveyors are commonly used in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities for moving boxes, packages, or other items along a straight path. Roller bed conveyors are particularly useful for handling lightweight to moderately heavy loads and can be configured in various layouts, including straight lines, curves, and inclines.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Low friction and smooth movement of materials due to the rolling action.
Ability to handle a wide range of product sizes and weights.
Versatile configurations, including curves and inclines.
Relatively low maintenance requirements.
Efficient use of floor space compared to other conveyor types.
Disadvantages:
Limited load capacities compared to some other conveyor types.
Potential for items to become stuck or misaligned on the rollers.
Noisy operation, especially with heavier loads.
Potential safety hazards if fingers or loose clothing get caught between rollers.
Higher initial cost compared to some simpler conveyor systems.
Flat Belt Conveyors
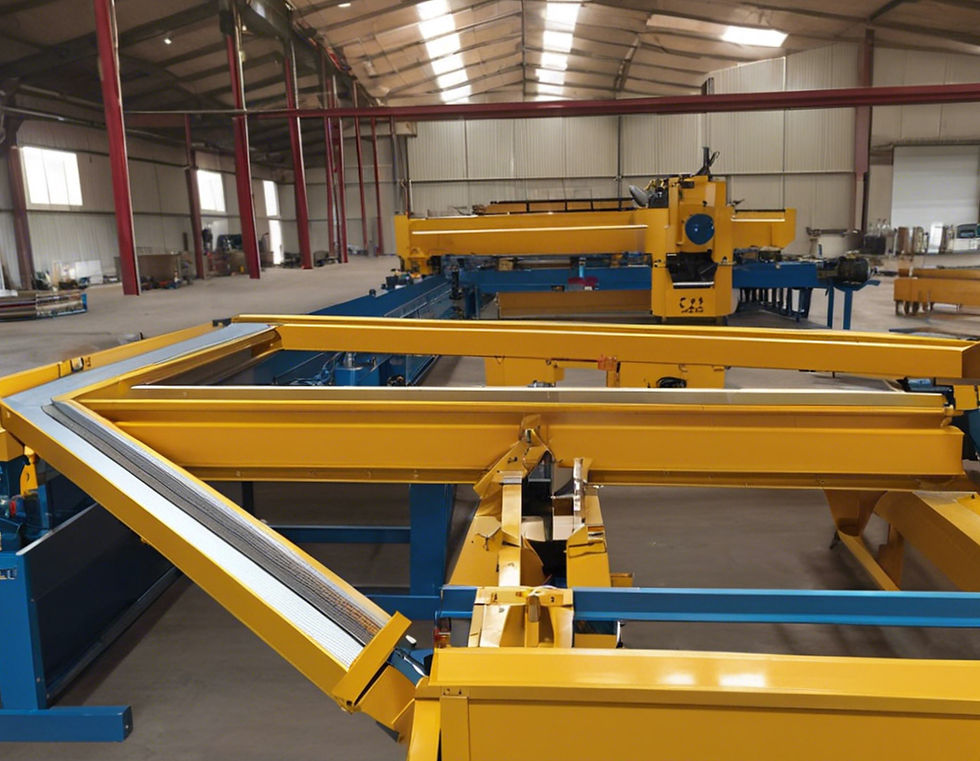

Description and Applications:
Flat belt conveyors are one of the most common and versatile types of conveyor systems. They consist of a flat, continuous belt that runs over a series of rollers or pulleys. The belt is typically made of materials such as rubber, PVC, or fabric, and can be reinforced with steel cables or cords for added strength and durability.
Flat belt conveyors are widely used in various industries for transporting a wide range of materials, including boxes, cartons, bags, and bulk materials. They are commonly found in warehouses, distribution centers, airports, and manufacturing facilities. These conveyors are particularly suitable for handling lightweight to moderately heavy loads over short to medium distances.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Versatility: Flat belt conveyors can handle a variety of materials, sizes, and weights, making them suitable for many applications.
Cost-effectiveness: They are generally less expensive to purchase and maintain compared to other conveyor types.
Simple design: The straightforward design of flat belt conveyors makes them easy to install, operate, and maintain.
Smooth operation: The flat surface of the belt allows for smooth and gentle product handling, reducing the risk of damage.
Disadvantages:
Limited load capacity: Flat belt conveyors have a lower load capacity compared to other conveyor types, such as roller or chain conveyors.
Belt tracking issues: If not properly aligned and tensioned, the belt can wander or drift, leading to potential product spillage or conveyor damage.
Limited incline capability: While some flat belt conveyors can handle slight inclines, they are generally not suitable for steep inclines or declines.
Potential product jamming: If not designed correctly, products can become jammed or stuck on the belt, causing operational disruptions.
Specialty Conveyor Belts
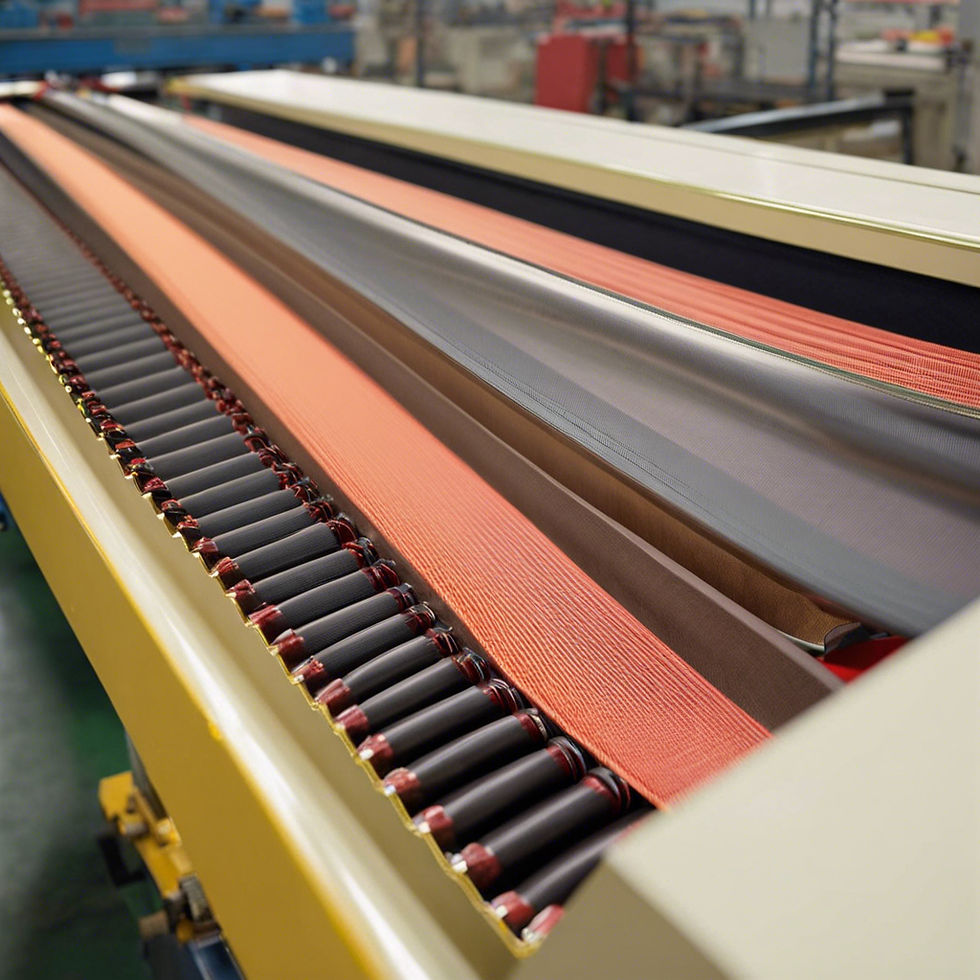

Specialty conveyor belts are designed for unique applications or environments that require specific features or capabilities beyond what standard conveyor belts can offer. These specialized belts come in various types, each engineered to meet specific industrial needs. Here are some common types of specialty conveyor belts:
Fiberglass Conveyor Belts

Fiberglass conveyor belts are made from woven fiberglass strands coated with a protective resin or elastomer. These belts are known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability. They are commonly used in high-temperature environments, such as foundries, glass manufacturing, and heat-treating processes.
Applications:
Handling hot materials
Furnace loading and unloading
Heat-treating operations
Advantages:
Excellent heat resistance (up to 500°C)
High tensile strength
Resistant to chemicals and abrasion
Disadvantages:
Limited flexibility
Higher cost compared to standard belts
Metal Nub Conveyor Belts
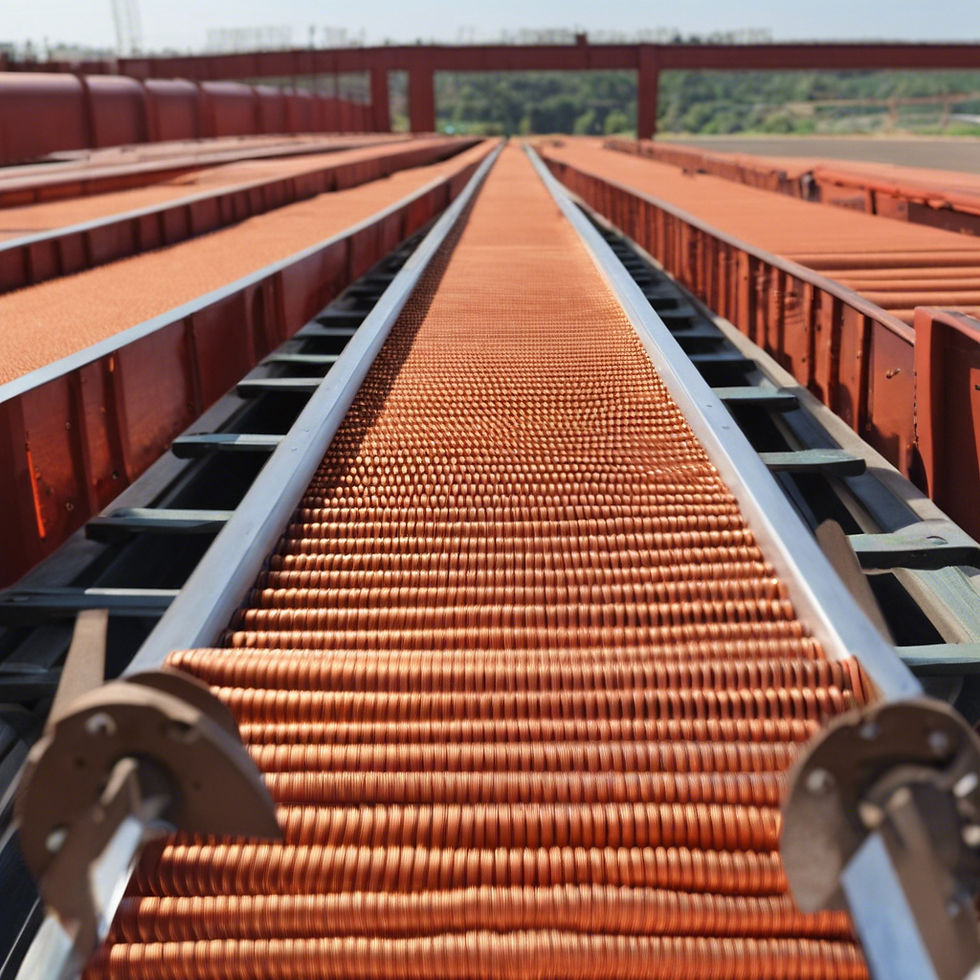

Metal nub conveyor belts feature a series of small, raised metal nubs or cleats on the belt surface. These nubs provide excellent traction and grip, preventing materials from slipping or sliding during transport.
Applications:
Handling heavy or irregular-shaped items
Inclined or declined conveying
Packaging and bottling lines
Advantages:
Superior grip and traction
Prevents product slippage
Durable and long-lasting
Disadvantages:
Potential for product damage with delicate items
Noisy operation
Limited flexibility
Narrow-Width Conveyor Belts

As the name suggests, narrow-width conveyor belts are designed for applications where space is limited or where only a small conveying area is required. These belts typically range from 2 inches to 12 inches in width.
Applications:
Packaging and labeling lines
Electronic component assembly
Pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing
Advantages:
Space-saving design
Efficient use of floor space
Suitable for small or delicate products
Disadvantages:
Limited capacity compared to wider belts
May require additional support for heavier loads
Back-Lit Conveyor Belts
Back-lit conveyor belts feature a translucent or transparent belt surface that allows light to pass through. These belts are often used in combination with specialized lighting systems or cameras for inspection or sorting applications.
Applications:
Product inspection and quality control
Sorting and grading of products
Automated vision systems
Advantages:
Improved visibility and inspection capabilities
Enhances accuracy in sorting and grading
Suitable for delicate or fragile products
Disadvantages:
Higher initial cost due to specialized components
Potential for light degradation over time
Limited load capacity compared to standard belts
Vacuum Conveyor Belts

Vacuum conveyor belts are designed to transport lightweight or delicate materials using a vacuum system. The belt surface is perforated, allowing air to be drawn through the holes, creating a suction effect that holds the materials in place during transport.
Applications:
Handling lightweight or fragile items
Printed circuit board assembly
Textile and paper industries
Advantages:
Gentle handling of delicate materials
Prevents product movement or shifting
Suitable for clean room environments
Disadvantages:
Limited load capacity
Requires a vacuum system and additional equipment
Potential for clogging or blockages
Magnetic Conveyor Belts

Magnetic conveyor belts incorporate powerful magnets into the belt surface, allowing them to transport ferrous (iron-containing) materials securely. These belts are often used in metalworking, recycling, and mining industries.
Applications:
Handling ferrous metals and scrap
Metal stamping and forming operations
Recycling and sorting facilities
Advantages:
Secure transport of ferrous materials
Prevents product slippage or movement
Suitable for harsh environments
Disadvantages:
Limited to ferrous materials only
Potential for product damage or scratching
High initial cost due to specialized components
Sandwich Conveyor Belts

Sandwich conveyor belts feature a unique construction with two outer layers of material sandwiching a middle layer of a different material. This design allows for a combination of properties, such as strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance.
Applications:
Food processing and packaging
Pharmaceutical manufacturing
Chemical and industrial applications
Advantages:
Customizable properties based on material combinations
Improved durability and longevity
Suitable for a wide range of applications
Disadvantages:
Higher cost compared to single-layer belts
Potential for delamination or separation of layers
Limited flexibility in some configurations
These are just a few examples of the many types of specialty conveyor belts available. Each type is designed to address specific challenges or requirements, offering unique advantages and capabilities for various industrial applications.
Materials Used in Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts are available in a variety of materials, each offering unique properties and benefits suited for different applications. The choice of material plays a crucial role in ensuring the conveyor belt's durability, load-bearing capacity, and compatibility with the products being transported. Here are some common materials used in conveyor belts:
Plastic
Plastic conveyor belts, such as those made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene, or polyurethane, are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to clean. They are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industries where sanitation is a priority. Plastic belts can be smooth or textured, and some types offer static dissipation properties.
Metal
Metal conveyor belts, typically constructed from stainless steel or aluminum, offer exceptional strength and durability. They are resistant to extreme temperatures, abrasion, and chemicals, making them ideal for harsh environments like foundries, steel mills, and mining operations. Metal belts can handle heavy loads and are often used in applications where heat resistance is essential.
Rubber
Rubber conveyor belts are known for their excellent traction, shock absorption, and resistance to cuts and tears. They are commonly used in applications involving heavy or abrasive materials, such as in quarries, mines, and construction sites. Rubber belts can also be designed with specific properties, such as heat resistance, oil resistance, or flame retardancy, to meet specific operational requirements.
Fabric
Fabric conveyor belts, made from materials like cotton, nylon, or polyester, offer flexibility and resistance to stretching and fraying. They are commonly used in light-duty applications, such as package handling, textile industries, and printing operations. Fabric belts can be coated with various materials, like PVC or silicone, to enhance their properties and increase their service life.
Leather
Leather conveyor belts are prized for their durability, strength, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. They are often used in industries like tanning, woodworking, and metalworking, where they can withstand harsh conditions and heavy loads. Leather belts are also preferred in applications where a smooth surface is required, such as in printing or food processing.
The choice of conveyor belt material depends on factors such as the type of products being transported, the environmental conditions, load requirements, and specific industry standards or regulations. Manufacturers often offer custom-engineered belts tailored to meet the unique needs of various applications, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
How Conveyor Belts Work
Conveyor belts are deceptively simple systems that rely on a few key mechanical components to transport materials from one point to another. At their core, conveyor belts consist of a continuous loop of durable material that rotates around a series of pulleys and rollers.
The driving force behind a conveyor belt is typically an electric motor, which powers one or more of the pulleys. These pulleys are strategically placed at either end of the conveyor belt's path and are responsible for rotating the belt in a continuous loop. As the motor turns the pulley, the belt's friction against the pulley's surface causes it to move in the desired direction.
Rollers play a crucial role in supporting the weight of the conveyor belt and the materials it carries. These cylindrical components are spaced at regular intervals along the length of the conveyor belt's path, providing a smooth and low-friction surface for the belt to glide over. Rollers not only reduce the overall resistance on the belt but also help maintain its alignment and prevent sagging or uneven wear.
The operational principles of conveyor belts are based on the careful coordination of these mechanical components. The motor's power is transmitted through the pulleys, which in turn drive the belt's movement. The rollers support the belt's weight and facilitate its smooth and efficient travel, allowing it to transport materials continuously and reliably.
By adjusting the speed of the motor, the conveyor belt's pace can be controlled, enabling it to handle a wide range of material flow rates. Additionally, the placement and configuration of the pulleys and rollers can be customized to accommodate specific operational requirements, such as inclines, declines, or horizontal turns.
Applications of Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts are ubiquitous in various industries due to their versatility and ability to streamline material handling processes. Here are some key applications across different sectors:
Manufacturing
In manufacturing facilities, conveyor belts play a crucial role in transporting raw materials, work-in-progress components, and finished goods. They facilitate efficient assembly lines, enabling smooth movement of products through various stages of production. Automotive, electronics, and consumer goods manufacturing heavily rely on conveyor systems for their operations.
Warehousing and Distribution
Warehouses and distribution centers utilize conveyor belts extensively to move goods from receiving areas to storage locations and then to shipping docks. Automated conveyor systems help streamline order fulfillment processes, improving accuracy and speed. Major e-commerce and logistics companies depend on advanced conveyor belt systems to handle high volumes of packages and shipments.
Food Processing
The food and beverage industry requires strict hygiene standards, making sanitary and washdown conveyor belts essential. These belts are designed to withstand frequent cleaning and sanitization processes, ensuring food safety. They are commonly used for transporting raw ingredients, packaging materials, and finished food products.
Logistics and Parcel Handling
Courier and parcel delivery services rely heavily on conveyor belt systems to sort, route, and load packages efficiently. High-speed sortation systems and inclined conveyors help streamline the movement of parcels through distribution hubs, ensuring timely delivery to customers.
Case Study: Automotive Assembly Line
In a large automotive manufacturing plant, a complex network of conveyor belts is used to transport vehicle components and subassemblies through various stations. Roller bed conveyors move heavy engine blocks and transmissions, while modular belt conveyors transport smaller parts like wiring harnesses and interior trim pieces. Curved and inclined conveyors facilitate smooth transitions between different assembly stages, enabling a continuous flow of production.
Case Study: E-Commerce Fulfillment Center
A leading e-commerce company's fulfillment center utilizes a highly automated conveyor belt system to handle millions of orders daily. Packages are sorted and routed using high-speed sortation conveyors, while flat belt conveyors transport them to designated shipping areas. Sanitary and washdown conveyors are used in the food and personal care sections, ensuring proper hygiene standards are met.
These examples illustrate the versatility and essential role of conveyor belts in supporting efficient material handling processes across various industries, enabling increased productivity, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Standards and Regulations
Conveyor belts are critical components in many industrial operations, and as such, they are subject to various standards and regulations to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance. These standards are set forth by organizations such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA), and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
The FDA regulates conveyor belts used in the food processing industry to ensure they meet strict hygiene and sanitation requirements. Conveyor belts in this sector must be made of food-grade materials, easy to clean and sanitize, and resistant to bacterial growth. Compliance with FDA regulations is crucial to prevent contamination and maintain food safety.
MSHA sets standards for conveyor belts used in mining operations, focusing on factors such as belt strength, fire resistance, and proper installation and maintenance. These regulations aim to prevent accidents, injuries, and potential disasters in the hazardous mining environment.
OSHA, on the other hand, establishes general safety standards for conveyor belts across various industries. These standards cover aspects like guarding, emergency stops, proper training for operators, and regular inspections to identify and mitigate potential hazards.
Compliance with these standards and regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for ensuring the safety of workers, protecting the environment, and maintaining the integrity and efficiency of operations. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, legal consequences, and potential shutdowns, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Manufacturers, suppliers, and end-users of conveyor belts must stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and implement comprehensive safety programs, regular maintenance schedules, and employee training to ensure full compliance. By adhering to these standards, businesses can create a safer working environment, minimize risks, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Conclusion
Conveyor belts are an essential component in various industries, playing a crucial role in material handling and transportation. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored the different types of conveyor belts, their applications, materials, and operational principles.
One of the key takeaways is that each type of conveyor belt offers unique advantages and is designed to address specific requirements. From the versatile roller bed conveyors to the specialized sanitary and washdown conveyors, the choice of conveyor belt can significantly impact operational efficiency, productivity, and compliance with industry standards.
When selecting a conveyor belt, it is essential to consider factors such as the nature of the materials being transported, the required throughput, the layout of the facility, and any specific environmental or regulatory considerations. Choosing the right conveyor belt can optimize material flow, reduce downtime, and ensure safe and hygienic operations.
Investing in the appropriate conveyor belt system can yield long-term benefits, including increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and improved overall operational performance. By carefully evaluating your specific needs and consulting with experts in the field, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your operational goals and maximizes your return on investment.
Remember, the conveyor belt is a critical component of your material handling system, and selecting the right one can significantly impact your business's success. Take the time to explore the options available, and don't hesitate to seek professional advice to ensure you make the best choice for your unique requirements.





Comments